Understanding Machine Translation and its Use Cases: Pros, Cons, and Real-World Examples
Machine Translation (MT) is revolutionizing global communication by enabling automatic translation of text or speech from one language into another using advanced artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) techniques. As businesses and individuals operate more globally, understanding the capabilities, limitations, and applications of machine translation is critical.
What Is Machine Translation?
Machine Translation refers to computer-generated language translation without human intervention. Early systems relied on rule-based or statistical methods, but today’s state-of-the-art solutions predominantly use Neural Machine Translation (NMT) powered by deep learning, neural networks, and transformer architectures. These advanced models analyze entire sentences and contexts to produce more fluent, natural, and accurate translations than ever before.
How Does Machine Translation Work?
At a high level, MT involves decoding the meaning of the source language text and encoding it into the target language. Modern NMT systems tokenize input text into smaller pieces called tokens, convert them into numerical vectors (embeddings), then use attention mechanisms to weigh word relationships across the sentence before generating the final output in the target language. See our supported languages.
Use Cases of Machine Translation
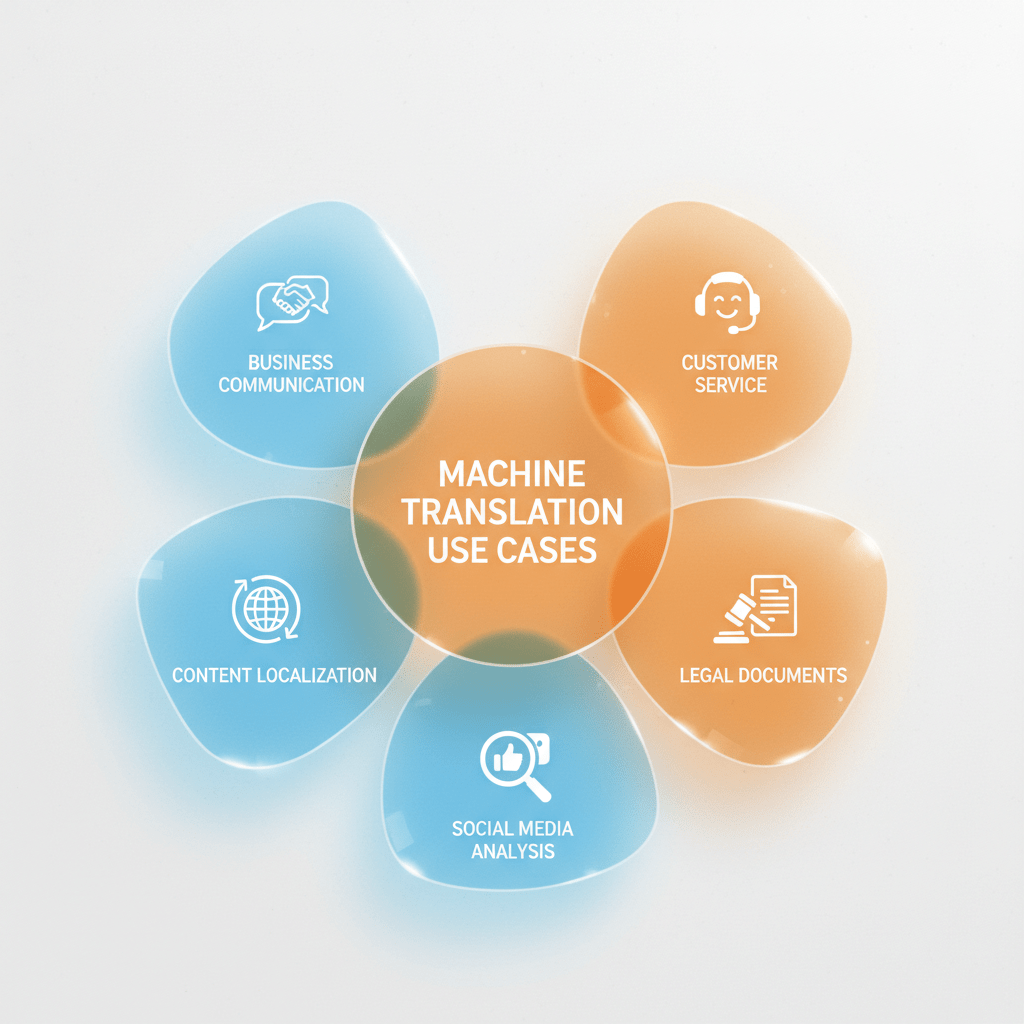
Machine translation is applied in various domains to break language barriers efficiently and scalably:
Internal Communication: Multinational companies translate presentations, emails, and bulletins instantly for diverse teams, reducing language gaps.
External Communication: Customer support and partner communications use MT for real-time translation of queries and documentation.
Content Localization: Websites, marketing materials, and e-commerce product listings are translated rapidly to customize content for local audiences.
Data Analysis: Huge volumes of user-generated multilingual text on social media and review sites are translated automatically for sentiment analysis.
Legal & Financial Operations: Machine translation speeds up contract reviews, compliance documentation, and financial reports, assisting cross-border operations.
Customer Service Automation: Live chatbots utilize MT to respond accurately in multiple languages, enhancing customer experience without expanding staff.
Pros and Cons of Machine Translation
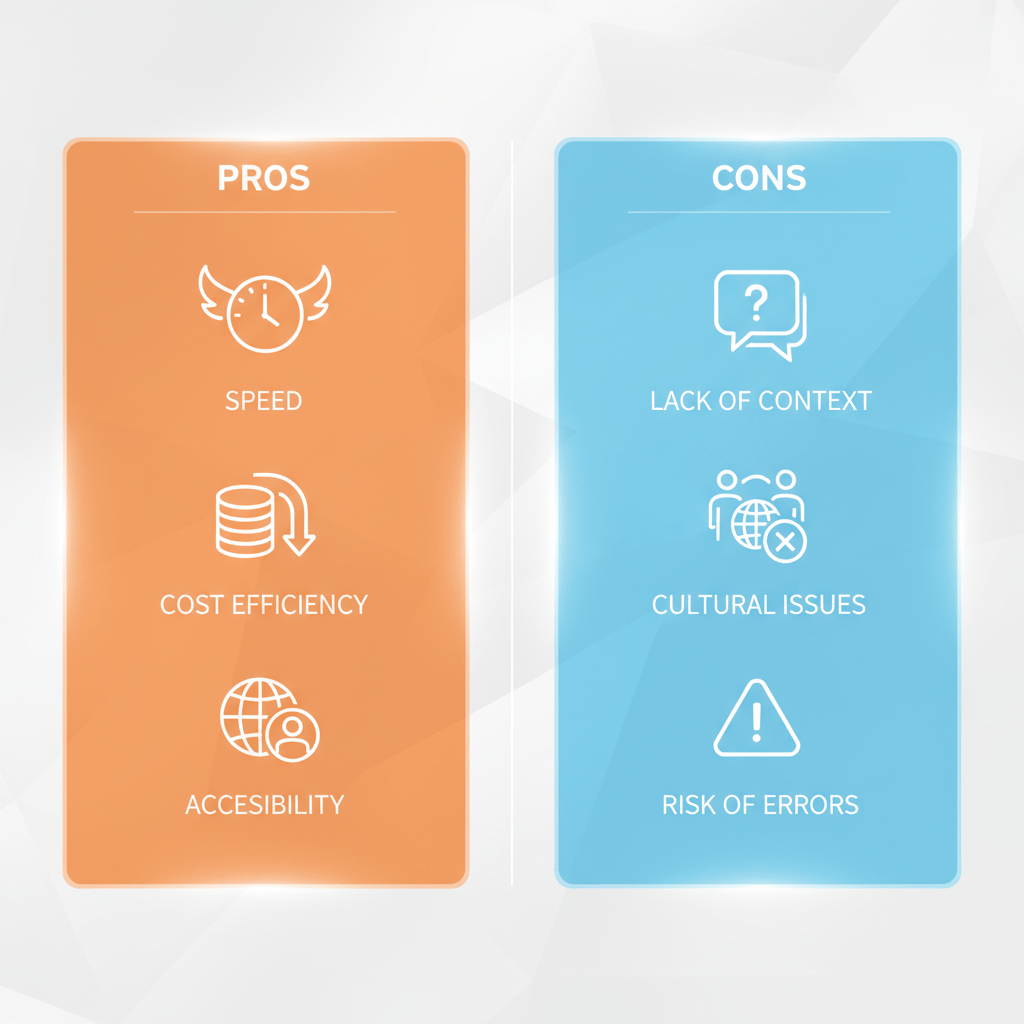
Pros of Machine Translation
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Speed | Translates large volumes quickly, meeting urgent needs. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces translation costs, especially for non-specialized content. |
| Availability | Accessible 24/7 to anyone with internet access. |
| Simple Translations | Excels at basic or repetitive content such as instructions and user guides. |
| Continuous Improvement | AI models improve constantly with new data and feedback. |
Cons of Machine Translation
| Disadvantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Lack of Contextualization | Often misses nuances like idioms, tone, and cultural intricacies. |
| Limited Expertise | Struggles with specialized terminology or complex texts without customization. |
| Cultural Nuances | Challenges in adapting content culturally beyond literal translation. |
| Lack of Creativity | Cannot replace human ingenuity in transcreation or artistic text. |
| Risk of Misunderstandings | Incorrect translations can lead to miscommunication or reputational risks. |
Types of Machine Translation Approaches
Rule-Based MT: Uses predefined linguistic rules and dictionaries; predictable but labor-intensive to maintain.
Statistical MT: Learns from large bilingual datasets and calculates probabilities for translation choices; requires lots of data.
Neural MT (NMT): Uses deep neural networks to model language context and semantics, currently the most effective.
Hybrid MT: Combines multiple approaches to balance accuracy and efficiency.
Real-World Examples
Google Translate & DeepL: Popular neural MT platforms known for multi-language support and integration APIs.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Customer service bots translating user queries live into agents’ languages.
E-Commerce: Automated translation of product descriptions to broaden customer reach.
Legal Document Translation: Speeding contract reviews for cross-border legal teams with post-editing by professionals. See more on our Legal Document Translation Services page.
The Future of Machine Translation
Advances in AI, including large language models (LLMs) and generative AI, will further enhance accuracy, context understanding, and translation quality. However, human expertise remains essential for cultural adaptation, creative content, and critical business communications, ensuring machine translation and human translators operate in synergy.
Contact Us
Need assistance with your translation, Applied Lingo offers the best document translation services in the industry. Contact us today or request a free quote and our team will respond to you in less than 30 minutes.
Discover more information
What is machine translation? |AWS
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Machine Translation | Translations and Interpretations
The Difference Between Human and Machine Translation Unveiled | Applied Lingo